Mesh Topology
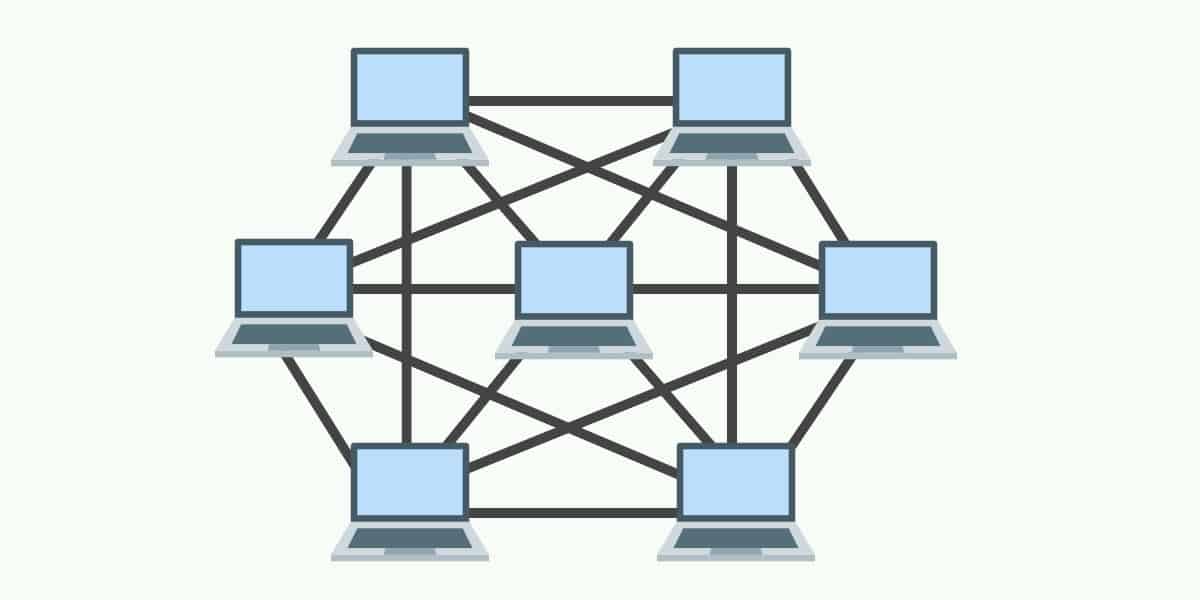
A mesh topology is a point-to-point connection where nodes are interconnected. In this form of topology, data is transmitted via two methods: routing and flooding. Routing is where nodes use routing logic to work out the shortest distance to the packet’s destination. In contrast flooding, data is sent to all nodes within the network. Flooding doesn’t require any form of routing logic to work.
There are two forms of mesh topology: partial mesh topology and full mesh topology. With partial mesh topology, most nodes are interconnected but there are a few which are only connected to two or three other nodes. A full mesh topology is where every node is interconnected.
Advantages
Mesh topologies are used first and foremost because they are reliable. The interconnectivity of nodes makes them extremely resistant to failures. There is no single machine failure that could bring down the entire network. The absence of a single point of failure is one of the reasons why this is a popular topology choice. This setup is also secure from being compromised.
Disadvantages
However, mesh topologies are far from perfect. They require an immense amount of configuration once they are deployed. The topological layout is more complex than many other topologies and this is reflected by how long it takes to set up. You’ll need to accommodate a whole host of new wiring which can add up to be quite expensive.
No comments:
Post a Comment